Bootstrap Columns Grid
Intro
In the recent couple years and most certainly the following ones to come the whole world of internet spreading more and more extensively across every kinds of devices and so currently basically half of the views of the web pages out there are made not on desktop computer and laptop computer display screens yet from various mobile products along with every kinds of small-sized display screen dimensions. In this degree assuming that a web page will not showcase correctly-- saying to resize and instantly find its own finest match on the device used its possibly will get explored away to become switched out by a mobile phone friendly webpage delivering quite similar services or product.
Furthermore-- the indexing mechanisms just like Google make the so called mobile-friendly test and indicate far down your pages inside of the search results. This lowering is even further supposing that the search is made by a mobile product-- the online search engines consider this particular situation pretty seriously. Hence not having a mobile friendly webpage practically points to not possessing a webpage in any way.
Tips on how to employ the Bootstrap Columns Content:
But just what really a page becoming responsive suggests-- generally-- fitting the whole width of the display screen which becomes showcased on introducing the elements in convenient and clear method at any size. To handle this the Bootstrap framework utilizes so called columns and breakpoints . In a several words the breakpoints are actually predefined screen widths at which a change occurs and the Bootstrap Columns Stack become transposed to ideally fit in preferable. The previous edition applied 4 breakpoints and the most new Bootstrap 4 framework launches one additional so they attain in fact five. Here they are having the maximum value they extend to. The particular boundary number in itself is fitting to the upcoming display size.
Extra small up to 34em ( or 544px) – up to Bootstrap 4 Alpha 5 had the -xs- infix. In Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 this infix is dropped so just the number follows;
Small – from 34em up to 48em ( or 768px ) – has the -sm- infix;
Medium – from 48em up to 62em ( or 992px ) – has the -md- infix;
Large – from 62em up to 75em ( 1200px ) - -lg- infix;
Extra large – 75em and everything above it – the new size in Bootstrap 4 – has the -xl- infix.
More suggestions
The horizontal zone in Bootstrap 4 framework gets distributed in 12 fragments identical in width-- these are the so called columns-- they all bringing the .col- prefix. Later comes the display size infix which specified down to what display screen scale the column component will span the defined number of columns. In the case that the screen sizing is smaller sized -- the column component utilizes the full display screen width-- just as if it was assigned .col-12 (.col-xs-12 up to Bootstrap 4 alpha 5).
Auto style columns
Implement breakpoint-specific column classes for equal-width columns. Incorporate any quantity of unit-less classes for every breakpoint you require and each and every Bootstrap Columns Tutorial is going to be the exact same width.
Identical size
For instance, here are two grid styles that apply to each gadget and viewport, from xs.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 2
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Initiating one column width
Auto-layout for flexbox grid columns additionally shows you can surely establish the width of one column and the others will quickly resize around it. You may work with predefined grid classes ( while shown below), grid mixins, or possibly inline widths. Bear in mind that the additional columns will resize no matter the width of the center column.

<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-6">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-5">
2 of 3 (wider)
</div>
<div class="col">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Variable size material
Working with the col- breakpoint -auto classes, columns may size on its own based on the typical width of its material. This is extremely handy having single line web content such as inputs, numbers, and the like. This particular, with horizontal alignment classes, is incredibly valuable for centralizing styles having irregular column sizes as viewport width changes.
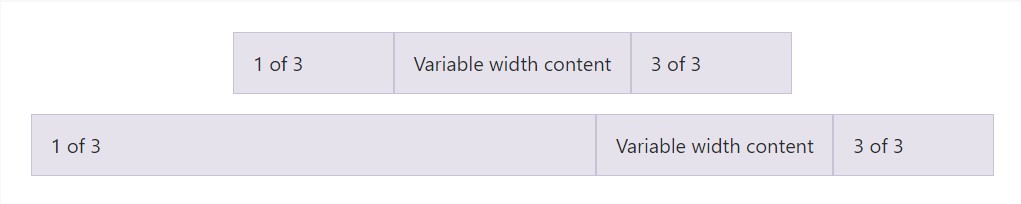
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-md-center">
<div class="col col-lg-2">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
1 of 3
</div>
<div class="col-12 col-md-auto">
Variable width content
</div>
<div class="col col-lg-2">
3 of 3
</div>
</div>
</div>Equivalent size multi-row
Generate equal-width columns which span multiple rows simply by filling in a .w-100 precisely where you want the columns to break to a new line. Make the gaps responsive simply by mixing the .w-100 by having some responsive screen utilities.
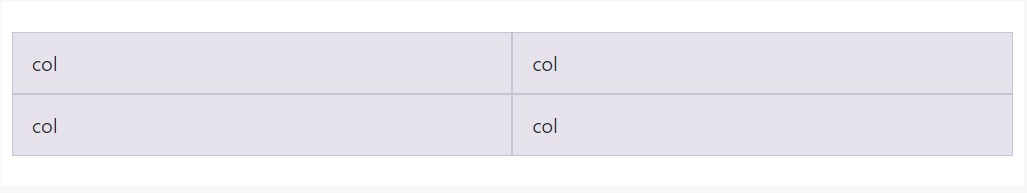
<div class="row">
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="w-100"></div>
<div class="col">col</div>
<div class="col">col</div>
</div>One more unique feature
Another new thing among the new Alpha 6 build of Bootstrap 4 is in the case that you incorporate simply a few .col-~ some number here ~ items spanning under 12 columns they will actually promote proportionally to get all of the space readily available on the row and are going to continue to be this way at any display width-- also under 32em.
Conclusions
So presently you understand the way in which the column components set up the structure as well as responsive behaviour of the Bootstrap system and all that is definitely left for you is making something truly fantastic by using them.
Examine several youtube video information about Bootstrap columns
Connected topics:
Bootstrap columns approved documentation

Responsive columns in Bootstrap
Complication with a heights of the Bootstrap columns